Abstract
Research Article
Impact of Calcium Phosphate Nanoparticles on Rice Plant
Hrishikesh Upadhyaya*, Lutfa Begum, Bishal Dey, P K Nath and S K Panda
Published: 21 February, 2017 | Volume 1 - Issue 1 | Pages: 001-010
Calcium phosphates are of great interest in medicine, biology, agriculture and materials sciences. The present study evaluates the effect of calcium phosphates nanoparticles on biochemical changes in rice. Nanoparticles increased the growth rate and affect the physiology of the plant. Calcium phosphate nanoparticles may help in the formulation of new nano growth promoter and nano-fertilizers for agricultural use. Therefore, it could potentially help in reduction of the quantity of fertilizer applied to crops and contributing to precision farming as it reduces fertilizer wastage and in turn environmental pollution due to agricultural malpractices. However, detail physiological and molecular understanding of its impact on rice crop plant is needed in future to validate its prospective application in agriculture.
Read Full Article HTML DOI: 10.29328/journal.jpsp.1001001 Cite this Article Read Full Article PDF
References
- Siddiqui MH, Al-Whaibi MH. Role of nano-SiO2 in germination of tomato (Lycopersicum esculentum seeds Mill.). Saudi J Biol Sci. 2014; 21: 13-17. Ref.: https://goo.gl/XDAqGr
- Jampílek J, Kráľová K. Application of nanotechnology in agriculture and food industry, its prospects and risks. Ecological Chemistry and Engineering Sci. 2015; 22: 321-361. Ref.: https://goo.gl/RlnGP0
- Giraldo JP, Landry MP, Faltermeier SM, McNicholas TP, Iverson NM, et al. Plant nanobionics approach to augment photosynthesis and biochemical sensing. Nature materials. 2014; 13: 400-408. Ref.: https://goo.gl/9Y7ois
- Mahajan S, Pandey GK, Tuteja N. Calcium-and salt-stress signaling in plants: shedding light on SOS pathway. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2008; 471: 146-158. Ref.: https://goo.gl/McGh5Z
- Lutts S, Kinet JM, Bouharmont J. Effects of salt stress on growth, mineral nutrition and proline accumulation in relation to osmotic adjustment in rice (Oryza sativa L.) cultivars differing in salinity resistance”. Plant Growth Regulation. 1996; 19: 207-218. Ref.: https://goo.gl/jPVuph
- Knight H. Calcium signaling during abiotic stress in plants. Int Rev Cytol. 1999; 195: 269-324. Ref.: https://goo.gl/uekn95
- Asano T, Hayashi N, Kobayashi M, Aoki N, Miyao A et al. A rice calcium‐dependent protein kinase OsCPK12 oppositely modulates salt‐stress tolerance and blast disease resistance. Plant J. 2012. 69: 26-36. Ref.: https://goo.gl/fSrGNV
- Pandey S, Zhang W, Assmann SM. Roles of ion channels and transporters in guard cell signal transduction. FEBS Lett. 2007; 581: 2325-2336. Ref.: https://goo.gl/1rabbB
- Das R, Pandey GK. Expressional Analysis and Role of Calcium Regulated Kinases in Abiotic Stress Signaling. Curr Genomics. 2014; 11: 2-13. Ref.: https://goo.gl/zDMq0l
- Sanders D, Pelloux J, Brownlee C, Harper JF. Calcium at the crossroads of signaling. Plant Cell. 2002; 14: S401-S417. Ref.: https://goo.gl/JSjWRv
- Trewavas AJ, Malhó R. Ca2+ signaling in plant cells: the big network. Curr Opin Plant Biol. 1998; 1: 428-433. Ref.: https://goo.gl/YZnYQ0
- McAinsh MR, Gray JE, Hetherington AM, Leckie CP, Ng C. Ca2+ signalling in stomatal guard cells. Biochem Soc Trans. 2000; 28: 476-481. Ref.: https://goo.gl/cjGBrI
- Luan S, Kudla J, Rodriguez-Concepcion M, Yalovsky S, Gruissem W. Calmodulins and calcineurin B-like proteins: calcium sensors for specific signal response coupling in plants. Plant Cell.2002; 14: S389-S400. Ref.: https://goo.gl/QwNHa1
- Snedden WA, Fromm H. Calmodulin as a versatile calcium signal transducer in plants. New Phytologist. 2001; 151: 35-66. Ref.: https://goo.gl/lrsOUx
- Zheng L, Hong F, Lu S, Liu C. Effect of nano-TiO2 on strength of naturally aged seeds and growth of spinach. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2005; 106: 279-297. Ref.: https://goo.gl/2hkbv6
- Galbraith DW. Nanobiotechnology: silica breaks through in plants. Nat Nanotechnol. 2007; 2: 272-273. Ref.: https://goo.gl/nTbR5o
- Mahajan P, Dhoke SK, Khanna AS. Effect of Nano-ZnO Particle Suspension on Growth of Mung (Vigna radiata) and Gram(Cicer arietinum) Seedlings Using Plant Agar Method. Journal of Nanotechnology. 2011; 2011: 1- 7. Ref.: https://goo.gl/gCskOk
- Boonyanitipong P, Kositsup B, Kumar P, Baruah S, Dutta J. Toxicity of ZnO and TiO2 Nanoparticles on Germinating Rice Seed Oryza sativa L. International Journal of Bioscience, Biochemistry Bioinformatics. 2011; 1: 282-285. Ref.: https://goo.gl/BNxhy2
- Liu R, Zhang H, Lal R. Effects of Stabilized Nanoparticles of Copper, Zinc, Manganese, and Iron Oxides in Low Concentrations on Lettuce (Lactuca sativa) Seed Germination: Nanotoxicants or Nanonutrients? Water, Air, and Soil Pollution. 2016; 227: 1-14. Ref.: https://goo.gl/0LWVpR
- Rane M, Bawskar M, Rathod D, Nagaonkar D, Rai M. Influence of calcium phosphate nanoparticles, Piriformospora indica and Glomus mosseae on growth of Zea mays. Advances in Natural Sciences: Nanoscience and Nanotechnology. 2015; 6: 045014. Ref.: https://goo.gl/X8XyRI
- Doke N. Involvement of superoxide anion generation in the hypersensitive response of potato tuber tissues to infection with an incompatable race of Phytophthora infestans and to the hyphal wall components. Physiological Plant Pathology. 1983; 23: 345-357. Ref.: https://goo.gl/cylbDi
- Lin CC, Kao CH. Cell wall peroxidase activity, hydrogen peroxide level and NaCl-inhibited root growth of rice seedlings. Plant and Soil. 2001; 230: 135-143. Ref.: https://goo.gl/R1Qa1g
- Zhang XZ. The measurement and mechanism of lipid peroxidation and SOD, POD and CAT activities in biological system. In Research Methodology of Crop physiology; Zhang, X.Z., Ed.; Agricultural Press: Beijing, China. 1992; 208-254.
- Griffith OW. Determination of glutathione and glutathione disulfide using glutathione reductase and 2-vinylpyridine. Anal Biochem. 1980; 106: 207-212. Ref.: https://goo.gl/mhMJT6
- Oser BL. Hawks physiological chemistry. McGraw Hill, NY, USA. 1979; 702-705.
- Abei H. Catalse in vitro. Methods Enzymol. 1984; 105: 121-126. Ref.: https://goo.gl/EK2zJg
- Chance B, Maehly AC. Assay of catalase and peroxidises. Methods Enzymology. 1955; 2: 764-775. Ref.: https://goo.gl/noFgcH
- Giannopolitis CN, Ries SK. Superoxide dismutase I. Occurrence in higher plants. Plant Physiol. 1997; 59: 309-314. Ref.: https://goo.gl/fVDTTx
- Smith IK, Vierheller TL, Thorne CA. Assay of glutathione reductase in crude tissue homogenates using 5, 51-dithiobis(2-nitrobenzoic acid). Anal Biochem. 1988; 175: 408-413. Ref.: https://goo.gl/EumbPn
- Upadhyaya H, Dutta BK, Panda SK. Zinc modulates drought induced biochemical damages in tea [Camellia sinensis (L) O Kuntze]. J Agric Food Chem. 2013; 61: 6660-6670. Ref.: https://goo.gl/979vsz
Figures:
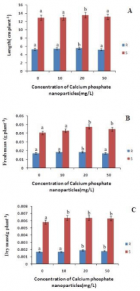
Figure 1
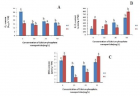
Figure 2
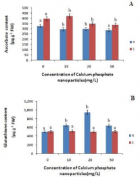
Figure 3
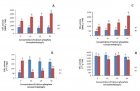
Figure 4
Similar Articles
-
Impact of Calcium Phosphate Nanoparticles on Rice PlantHrishikesh Upadhyaya*,Lutfa Begum,Bishal Dey,P K Nath,S K Panda. Impact of Calcium Phosphate Nanoparticles on Rice Plant. . 2017 doi: 10.29328/journal.jpsp.1001001; 1: 001-010
-
The Effects of Pharmacological Carbonic Anhydrase Suppression on Defence Responses of Potato Leaves To Phytophthora InfestansMagdalena Arasimowicz-Jelonek*,Jolanta Floryszak-Wieczorek. The Effects of Pharmacological Carbonic Anhydrase Suppression on Defence Responses of Potato Leaves To Phytophthora Infestans. . 2017 doi: 10.29328/journal.jpsp.1001002; 1: 011-025
-
Phytochemical content of leaf and stem of Marsilea quadrifolia (L.)Rajangam Udayakumar*,Karikalan Gopalakrishnan. Phytochemical content of leaf and stem of Marsilea quadrifolia (L.). . 2017 doi: 10.29328/journal.jpsp.1001003; 1: 026-037
-
Antagonistic features displayed by Plant Growth Promoting Rhizobacteria (PGPR): A ReviewMohsin Tariq*,Muhammad Noman,Temoor Ahmed,Amir Hameed,Natasha Manzoor,Marriam Zafar. Antagonistic features displayed by Plant Growth Promoting Rhizobacteria (PGPR): A Review . . 2017 doi: 10.29328/journal.jpsp.1001004; 1: 038-043
-
Wild-type Agrobacterium rhizogenes-mediated gene transfer in plants: Agrobacterium virulence and selection of transformantsShu Wei*,Muhammad Abdullah,Ferdinand L Shamalla,Mohammad M Rana. Wild-type Agrobacterium rhizogenes-mediated gene transfer in plants: Agrobacterium virulence and selection of transformants. . 2017 doi: 10.29328/journal.jpsp.1001005; 1: 044-051
-
Effects of Vochysia haenkeana extract on the neuromuscular blockade induced by Bothrops jararaca venom on chick biventer cervicis preparation in vitroYoko Oshima-Franco*,Fernanda Dias da Silva,Natália Tribuiani,Isadora Caruso Fontana Oliveira,Regina Yuri Hashimoto Miura,Rafael S Floriano,Márcio Galdino dos Santos,Sandro Rostelato-Ferreira. Effects of Vochysia haenkeana extract on the neuromuscular blockade induced by Bothrops jararaca venom on chick biventer cervicis preparation in vitro. . 2017 doi: 10.29328/journal.jpsp.1001006; 1: 052-058
-
HBV: Genomic Structure, HBVsAg Isolation and innovative Virotherapy Initiation in the Middle EastAboul-Ata E Aboul-Ata*,Essam M Janahi,I M El-Kalamawy,Kathleen Hefferon,Amal Mahmoud. HBV: Genomic Structure, HBVsAg Isolation and innovative Virotherapy Initiation in the Middle East . . 2017 doi: 10.29328/journal.jpsp.1001007; 1: 059-061
-
Physiological impact of Zinc nanoparticle on germination of rice (Oryza sativa L) seedUpadhyaya H*,Roy H,Shome S,Tewari S,Bhattacharya MK,Panda SK. Physiological impact of Zinc nanoparticle on germination of rice (Oryza sativa L) seed . . 2017 doi: 10.29328/journal.jpsp.1001008; 1: 062-070
-
Effects of Site Factors on the Clonal Growth of Phyllostachys bambusoides f. shouzhu YiXiaohong Gan*,Lijuan Chen,Cuibin Tang,Xia Zhang. Effects of Site Factors on the Clonal Growth of Phyllostachys bambusoides f. shouzhu Yi. . 2017 doi: 10.29328/journal.jpsp.1001009; 1: 071-079
-
Evaluation of genetic diversity in germplasm of paprika (Capsicum spp.) using random amplified polymorphic DNA (RAPD) markersRueda-Puente EO*,Renganathan P,Ruíz-Alvarado C,Hernández-Montiel LG,Prasath Duraisamy. Evaluation of genetic diversity in germplasm of paprika (Capsicum spp.) using random amplified polymorphic DNA (RAPD) markers. . 2017 doi: 10.29328/journal.jpsp.1001010; 1: 080-086
Recently Viewed
-
Sinonasal Myxoma Extending into the Orbit in a 4-Year Old: A Case PresentationJulian A Purrinos*, Ramzi Younis. Sinonasal Myxoma Extending into the Orbit in a 4-Year Old: A Case Presentation. Arch Case Rep. 2024: doi: 10.29328/journal.acr.1001099; 8: 075-077
-
Comparative Study of Cerebral Volumetric Variations in Patients with Schizophrenia with their Unaffected First-degree Relatives, using Magnetic Resonance Imaging Technique, a Case-control StudyMahdiye Fanayi,Mohammad Ali Oghabian*,Hamid Reza Naghavi,Hassan Farrahi. Comparative Study of Cerebral Volumetric Variations in Patients with Schizophrenia with their Unaffected First-degree Relatives, using Magnetic Resonance Imaging Technique, a Case-control Study. J Neurosci Neurol Disord. 2024: doi: 10.29328/journal.jnnd.1001088; 8: 001-007
-
Deciphering the Rosetta Stone - Trans-Mitral Doppler Patterns for a Simplified Study of Left Ventricular Systolic DysfunctionGeorge Thomas*. Deciphering the Rosetta Stone - Trans-Mitral Doppler Patterns for a Simplified Study of Left Ventricular Systolic Dysfunction. Int J Clin Anesth Res. 2023: doi: 10.29328/journal.ijcar.1001023; 7: 008-011
-
Gentian Violet Modulates Cytokines Levels in Mice Spleen toward an Anti-inflammatory ProfileSalam Jbeili, Mohamad Rima, Abdul Rahman Annous, Abdo Ibrahim Berro, Ziad Fajloun, Marc Karam*. Gentian Violet Modulates Cytokines Levels in Mice Spleen toward an Anti-inflammatory Profile. Arch Asthma Allergy Immunol. 2024: doi: 10.29328/journal.aaai.1001034; 8: 001-006
-
Detrimental Effects of Methylenetetrahydrofolate Reductase (MTHFR) Gene Polymorphism on Human Reproductive Health: A ReviewVandana Rai*,Pradeep Kumar. Detrimental Effects of Methylenetetrahydrofolate Reductase (MTHFR) Gene Polymorphism on Human Reproductive Health: A Review. Clin J Obstet Gynecol. 2025: doi: 10.29328/journal.cjog.1001182; 8: 007-014
Most Viewed
-
Evaluation of Biostimulants Based on Recovered Protein Hydrolysates from Animal By-products as Plant Growth EnhancersH Pérez-Aguilar*, M Lacruz-Asaro, F Arán-Ais. Evaluation of Biostimulants Based on Recovered Protein Hydrolysates from Animal By-products as Plant Growth Enhancers. J Plant Sci Phytopathol. 2023 doi: 10.29328/journal.jpsp.1001104; 7: 042-047
-
Sinonasal Myxoma Extending into the Orbit in a 4-Year Old: A Case PresentationJulian A Purrinos*, Ramzi Younis. Sinonasal Myxoma Extending into the Orbit in a 4-Year Old: A Case Presentation. Arch Case Rep. 2024 doi: 10.29328/journal.acr.1001099; 8: 075-077
-
Feasibility study of magnetic sensing for detecting single-neuron action potentialsDenis Tonini,Kai Wu,Renata Saha,Jian-Ping Wang*. Feasibility study of magnetic sensing for detecting single-neuron action potentials. Ann Biomed Sci Eng. 2022 doi: 10.29328/journal.abse.1001018; 6: 019-029
-
Pediatric Dysgerminoma: Unveiling a Rare Ovarian TumorFaten Limaiem*, Khalil Saffar, Ahmed Halouani. Pediatric Dysgerminoma: Unveiling a Rare Ovarian Tumor. Arch Case Rep. 2024 doi: 10.29328/journal.acr.1001087; 8: 010-013
-
Physical activity can change the physiological and psychological circumstances during COVID-19 pandemic: A narrative reviewKhashayar Maroufi*. Physical activity can change the physiological and psychological circumstances during COVID-19 pandemic: A narrative review. J Sports Med Ther. 2021 doi: 10.29328/journal.jsmt.1001051; 6: 001-007

HSPI: We're glad you're here. Please click "create a new Query" if you are a new visitor to our website and need further information from us.
If you are already a member of our network and need to keep track of any developments regarding a question you have already submitted, click "take me to my Query."