Abstract
Short Communication
MALDI-MSI method for the detection of large biomolecules in plant leaf tissue
Lilian ST Carmo, Daiane G Ribeiro, Eder A Barbosa, Luciano P Silva and Angela Mehta*
Published: 06 August, 2021 | Volume 5 - Issue 2 | Pages: 058-061
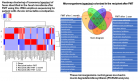
In this study we describe a method for the detection of biomolecules (in the polypeptide m/z range) directly from the surface of plant leaves by using Mass Spectrometry Imaging. The plant-pathogen interaction between Arabidopsis thaliana and the bacterium Xanthomonas campestris pv. campestris was analyzed by comparing infected and non-infected leaf discs submitted to mass spectrometry. The total surface area of ion distribution was calculated for both samples, revealing 23 ions, out of which 3 showed statistical significance. Although these ions were not identified, the results showed that this approach can be successfully applied for the detection of potential polypeptide biomarkers directly on leaf tissue, which is a major challenge in MALDI-Imaging studies.
Read Full Article HTML DOI: 10.29328/journal.jpsp.1001061 Cite this Article Read Full Article PDF
Keywords:
Mass spectrometry imaging; Plant-pathogen interaction; Protein biomarkers; Xanthomonas campestris pv. campestris; Arabidopsis thaliana
References
- Dueñas ME, Feenstra AD, Korte AR, Hinners P, Lee YJ. Cellular and Subcellular Level Localization of Maize Lipids and Metabolites Using High-Spatial Resolution Maldi Mass Spectrometry Imaging. Methods Mol Biol. 2018; 1676: 217-231.PubMed: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28986913/
- Solon EG, Schweitzer A, Stoeckli M, Prideaux B. Autoradiography, Maldi-Ms, and Sims-Ms Imaging in Pharmaceutical Discovery and Development. AAPS J. 2010; 12: 11-26.PubMed: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19921438/
- Groseclose MR, Andersson M, Hardesty WM, Caprioli RM. Identification of Proteins Directly from Tissue: In Situ Tryptic Digestions Coupled with Imaging Mass Spectrometry. J Mass Spectrometry. 2007; 42: 254-262.PubMed: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17230433/
- Michal A, Sabo J, Longuespée R. Microproteomic Sample Preparation. Proteomics. 2021: 2000318. PubMed: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33547857/
- Balluff B, Elsner M, Kowarsch A, Rauser S, Meding S, et al. Classification of Her2/Neu Status in Gastric Cancer Using a Breast-Cancer Derived Proteome Classifier. J Prote Res. 2010; 9: 6317-6322.PubMed: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21058730/
- Ermini L, Morganti E, Post A, Yeganeh B, Caniggia I, et al. Imaging Mass Spectrometry Identifies Prognostic Ganglioside Species in Rodent Intracranial Transplants of Glioma and Medulloblastoma. PLoS One. 2017; 12: e0176254.PubMed: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28463983/
- Ucal Y, Durer ZA, Atak H, Kadioglu E, Sahin B, et al. Ozpinar. Clinical Applications of Maldi Imaging Technologies in Cancer and Neurodegenerative Diseases. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta. 2017; 1865: 795-816. PubMed: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28087424/
- Jaegger CF, Negrão F, Assis DM, Belaz KRA, Angolini CFF, et al. Maldi Ms Imaging Investigation of the Host Response to Visceral Leishmaniasis. Mol Biosyst. 2017; 13: 1946-1953. PubMed: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28758666/
- Kaspar S, Peukert M, Svatos A, Matros A, Mock HP. Maldi-Imaging Mass Spectrometry - an Emerging Technique in Plant Biology. Proteomics. 2011; 11: 1840-1850.PubMed: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21462348/
- Sturtevant D, Lee YJ, Chapman KD. Matrix Assisted Laser Desorption/Ionization-Mass Spectrometry Imaging (Maldi-Msi) for Direct Visualization of Plant Metabolites in Situ. Curr Opin Biotechnol. 2016; 37: 53-60.PubMed: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26613199/
- Araújo FD, Araújo WL, Eberlin MN. Potential of Burkholderia Seminalis Tc3.4.2r3 as Biocontrol Agent against Fusarium Oxysporum Evaluated by Mass Spectrometry Imaging. J Am Society Mass Spectrometry. 2017; 28: 901-907.PubMed: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28194740/
- Kim W, Park JJ, Dugan FM, Peever TL, Gang DR, et al. Production of the Antibiotic Secondary Metabolite Solanapyrone a by the Fungal Plant Pathogen Ascochyta Rabiei During Fruiting Body Formation in Saprobic Growth. Environ Microbiol. 2017; 19: 1822-1835.PubMed: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28109049/
- Slazak B, Kapusta M, Malik S, Bohdanowicz J, Kuta E, et al. Immunolocalization of Cyclotides in Plant Cells, Tissues and Organ Supports Their Role in Host Defense. Planta. 2016; 244: 1029-1040.PubMed: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27394154/
- Klein AT, Yagnik GB, Hohenstein JD, Ji Z, Zi J, et al. Investigation of the Chemical Interface in the Soybean-Aphid and Rice-Bacteria Interactions Using Maldi-Mass Spectrometry Imaging. Anal Chem. 2015; 87: 5294-5301. PubMed: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25914940/
- Soares MS, da Silva DS, Forim MR, da Silva MF, Fernandes JB, et al. Machado. Quantification and Localization of Hesperidin and Rutin in Citrus Sinensis Grafted on C. Limonia after Xylella Fastidiosa Infection by Hplc-Uv and Maldi Imaging Mass Spectrometry. Phytochemistry. 2015; 115: 161-170. PubMed: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25749617/
- Julia G, Taylor NL, Millar AA. Matrix-Assisted Laser Desorption/Ionisation Mass Spectrometry Imaging and Its Development for Plant Protein Imaging. Plant Methods. 2011; 7: 21.PubMed: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21726462/
- Poth AG, Mylne JS, Grassl J, Lyons RE, Millar A, et al. Cyclotides Associate with Leaf Vasculature and Are the Products of a Novel Precursor in Petunia (Solanaceae). J Biol Chem. 2012; 287: 27033-27046.PubMed: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22700981/
- Erin G, Keller C, Jayaraman D, Maeda J, Sussman MR, et al. Examination of Endogenous Peptides in Medicago Truncatula Using Mass Spectrometry Imaging. J Prote Res. 2016; 15: 4403-4411.PubMed: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27726374/
- Eriksson C, Masaki N, Yao I, Hayasaka T, Setou M. Maldi Imaging Mass Spectrometry-a Mini Review of Methods and Recent Developments. Mass Spectrometry (Tokyo). 2013; 2: S0022.PubMed: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24349941/
- Longuespée R, Casadonte R, Kriegsmann M, Pottier C, Picard de Muller G, et al. Maldi Mass Spectrometry Imaging: A Cutting-Edge Tool for Fundamental and Clinical Histopathology. Proteomics Clin Appl. 2016; 10: 701-719.PubMed: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27188927/
- Attia Ahmed S, Schroeder KA, Seeley EH, Wilson KJ, Hammer ND, et al. Monitoring the Inflammatory Response to Infection through the Integration of Maldi Ims and Mri. Cell Host & Microbe. 2010; 11: 664-673. PubMed: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22704626/
- Alves BE, Bonfim MF, Bloch C, Engler G, Rocha T, et al. Imaging Mass Spectrometry of Endogenous Polypeptides and Secondary Metabolites from Galls Induced by Root-Knot Nematodes in Tomato Roots. Molecular Plant-Microbe Interactions. 2018; 31: 1048-1059. PubMed: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29663868/
- Boughton Berin A, Thinagaran D, Sarabia D, Bacic A, Roessner U. Mass Spectrometry Imaging for Plant Biology: A Review. Phytochem Rev. 2016; 15: 445-488.PubMed: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27340381/
- Yonghui D, Li B, Malitsky S, Rogachev I, Aharoni A, et al. Sample Preparation for Mass Spectrometry Imaging of Plant Tissues: A Review. Front Plant Sci. 2016; 7: 60.PubMed: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26904042/
- Nanna B, Li B, D'Alvise J, Janfelt C. Mass Spectrometry Imaging of Plant Metabolites – Principles and Possibilities. Nat Prod Rep. 2014; 31: 818-837.PubMed: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24452137/
- Debois D, Jourdan E, Smargiasso N, Thonart P, De Pauw E, et al. Spatiotemporal Monitoring of the Antibiome Secreted by Bacillus Biofilms on Plant Roots Using Maldi Mass Spectrometry Imaging. Anal Chem. 2014; 86: 4431-4438. PubMed: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24712753/
Figures:
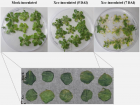
Figure 1
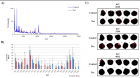
Figure 2
Similar Articles
-
Role of polyamine metabolism in plant pathogen interactionsMagda Pal*,Tibor Janda. Role of polyamine metabolism in plant pathogen interactions. . 2017 doi: 10.29328/journal.jpsp.1001012; 1: 095-100
-
Role of HECT ubiquitin protein ligases in Arabidopsis thalianaYing Miao*,Wei Lan,Weibo Ma. Role of HECT ubiquitin protein ligases in Arabidopsis thaliana. . 2018 doi: 10.29328/journal.jpsp.1001016; 2: 020-030
-
Evaluation of cold response in Ilex paraguariensisCristian Antonio Rojas*,Sandonaid Andrei Geisler,Carina Francisca Argüelles. Evaluation of cold response in Ilex paraguariensis. . 2019 doi: 10.29328/journal.jpsp.1001026; 3: 009-012
-
Cloning and Characterization of a Pseudo-Response Regulator 7 (PRR7) Gene from Medicago Sativa Involved In Regulating the Circadian ClockWeifeng Nian*,Yilin Shen. Cloning and Characterization of a Pseudo-Response Regulator 7 (PRR7) Gene from Medicago Sativa Involved In Regulating the Circadian Clock. . 2019 doi: 10.29328/journal.jpsp.1001032; 3: 056-061
-
MALDI-MSI method for the detection of large biomolecules in plant leaf tissueLilian ST Carmo,Daiane G Ribeiro,Eder A Barbosa,Luciano P Silva,Angela Mehta*. MALDI-MSI method for the detection of large biomolecules in plant leaf tissue. . 2021 doi: 10.29328/journal.jpsp.1001061; 5: 058-061
-
Flashes of UV-C light are perceived by UVR8, the photoreceptor of UV-B lightJawad Aarrouf*,Douae Ben Hdech,Alice Diot,Isabelle Bornard,Lauri Félicie,Laurent Urban*. Flashes of UV-C light are perceived by UVR8, the photoreceptor of UV-B light. . 2022 doi: 10.29328/journal.jpsp.1001089; 6: 151-153
-
Snapshot of the Involvement of Glutathione in Plant-Pathogen InteractionsAparupa Bose Mazumdar Ghosh, Sharmila Chattopadhyay*. Snapshot of the Involvement of Glutathione in Plant-Pathogen Interactions. . 2023 doi: 10.29328/journal.jpsp.1001103; 7: 039-041
Recently Viewed
-
Environmental Factors Affecting the Concentration of DNA in Blood and Saliva Stains: A ReviewDivya Khorwal*, GK Mathur, Umema Ahmed, SS Daga. Environmental Factors Affecting the Concentration of DNA in Blood and Saliva Stains: A Review. J Forensic Sci Res. 2024: doi: 10.29328/journal.jfsr.1001057; 8: 009-015
-
Markov Chains of Molecular Processes of Biochemical MaterialsOrchidea Maria Lecian*. Markov Chains of Molecular Processes of Biochemical Materials. Int J Phys Res Appl. 2024: doi: 10.29328/journal.ijpra.1001076; 7: 001-005
-
Generation of Curved Spacetime in Quantum FieldSarfraj Khan*. Generation of Curved Spacetime in Quantum Field. Int J Phys Res Appl. 2024: doi: 10.29328/journal.ijpra.1001077; 7: 006-009
-
Optimizing Milk Safety: Applying Nuclear Techniques in X-ray Fluorescence Spectroscopy for Heavy Metal Quantification in Powdered Milk Consumed in SenegalPapa Macoumba Faye*, Djicknack Dione, Oumar Ndiaye, Moussa Hamady SY, Nogaye Ndiaye, Alassane Traore, Ababacar Sadikhe Ndao. Optimizing Milk Safety: Applying Nuclear Techniques in X-ray Fluorescence Spectroscopy for Heavy Metal Quantification in Powdered Milk Consumed in Senegal. Int J Phys Res Appl. 2024: doi: 10.29328/journal.ijpra.1001078; 7: 010-015
-
Thermoelectric Materials Based on Lead Telluride and Prospects for their Practical ApplicationYuriy Pavlovskyy*, Nadiya Pavlovska. Thermoelectric Materials Based on Lead Telluride and Prospects for their Practical Application. Int J Phys Res Appl. 2024: doi: 10.29328/journal.ijpra.1001079; 7: 016-018
Most Viewed
-
Evaluation of Biostimulants Based on Recovered Protein Hydrolysates from Animal By-products as Plant Growth EnhancersH Pérez-Aguilar*, M Lacruz-Asaro, F Arán-Ais. Evaluation of Biostimulants Based on Recovered Protein Hydrolysates from Animal By-products as Plant Growth Enhancers. J Plant Sci Phytopathol. 2023 doi: 10.29328/journal.jpsp.1001104; 7: 042-047
-
Sinonasal Myxoma Extending into the Orbit in a 4-Year Old: A Case PresentationJulian A Purrinos*, Ramzi Younis. Sinonasal Myxoma Extending into the Orbit in a 4-Year Old: A Case Presentation. Arch Case Rep. 2024 doi: 10.29328/journal.acr.1001099; 8: 075-077
-
Feasibility study of magnetic sensing for detecting single-neuron action potentialsDenis Tonini,Kai Wu,Renata Saha,Jian-Ping Wang*. Feasibility study of magnetic sensing for detecting single-neuron action potentials. Ann Biomed Sci Eng. 2022 doi: 10.29328/journal.abse.1001018; 6: 019-029
-
Pediatric Dysgerminoma: Unveiling a Rare Ovarian TumorFaten Limaiem*, Khalil Saffar, Ahmed Halouani. Pediatric Dysgerminoma: Unveiling a Rare Ovarian Tumor. Arch Case Rep. 2024 doi: 10.29328/journal.acr.1001087; 8: 010-013
-
Physical activity can change the physiological and psychological circumstances during COVID-19 pandemic: A narrative reviewKhashayar Maroufi*. Physical activity can change the physiological and psychological circumstances during COVID-19 pandemic: A narrative review. J Sports Med Ther. 2021 doi: 10.29328/journal.jsmt.1001051; 6: 001-007

HSPI: We're glad you're here. Please click "create a new Query" if you are a new visitor to our website and need further information from us.
If you are already a member of our network and need to keep track of any developments regarding a question you have already submitted, click "take me to my Query."